Augmented Reality: Redefining the Digital World
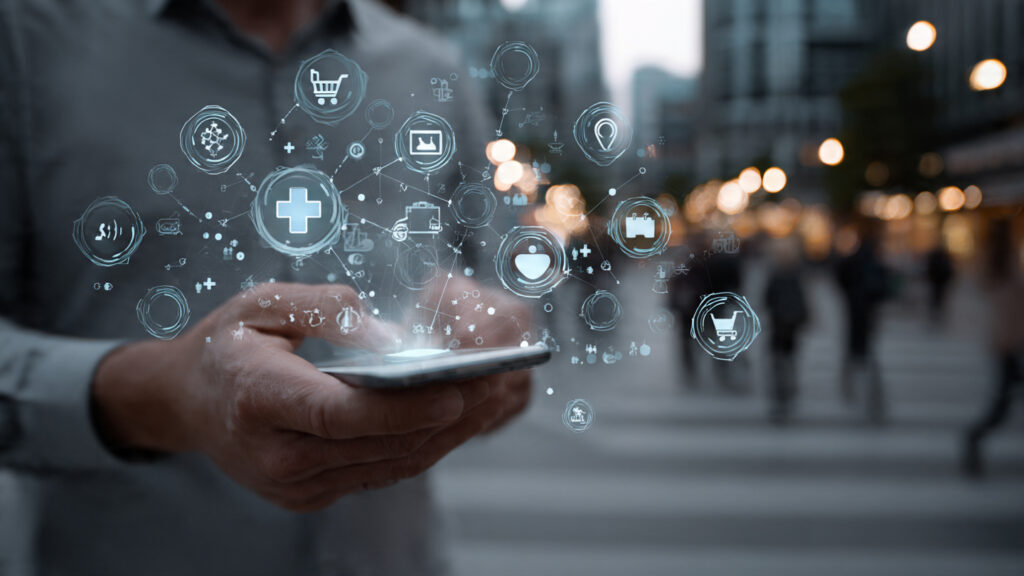

AR is no longer a futuristic idea reserved for science fiction. Instead, it has quietly become part of everyday digital experiences. From mobile apps and social media filters to industrial training and healthcare simulations, augmented reality is reshaping how humans interact with information. When combined with artificial intelligence, augmented reality moves beyond visual effects and becomes an intelligent, adaptive layer on top of the real world.
In the AI era, augmented reality is not just about adding digital elements to physical spaces. Rather, it is about understanding environments, predicting user intent, and responding intelligently in real time. This shift transforms AR into one of the most powerful technologies driving the next phase of digital transformation.
What Is Augmented Reality?
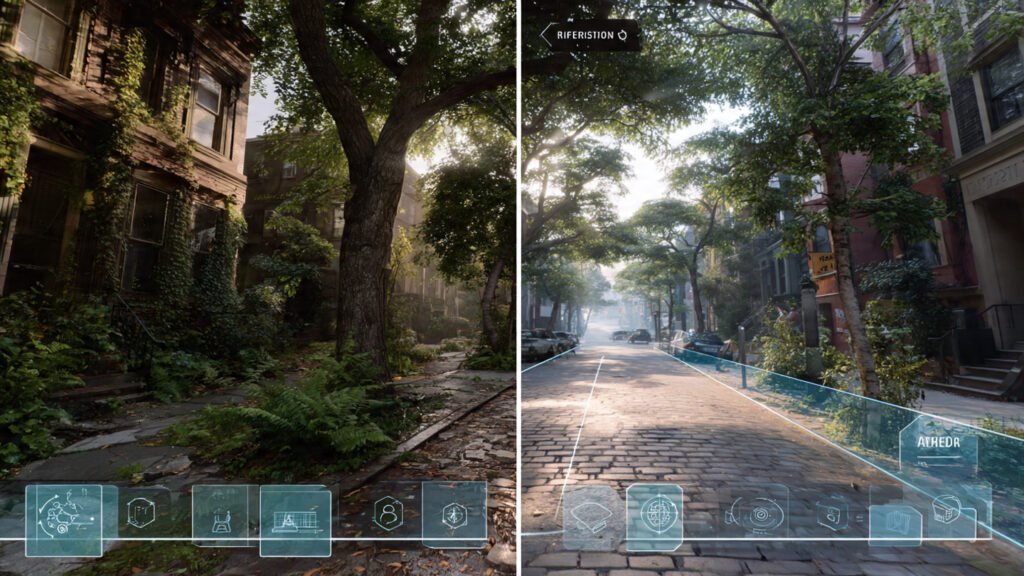
Augmented reality refers to technology that overlays digital content onto the real world in real time. Unlike virtual reality, which replaces the physical environment entirely, augmented reality enhances what already exists. Through smartphones, smart glasses, tablets, and wearable devices, users see digital information blended seamlessly with their surroundings.
However, modern augmented reality goes far beyond simple overlays. With AI integration, AR systems can recognize objects, understand spatial depth, track movement, and adapt content dynamically. As a result, the experience feels natural rather than artificial. This ability to merge physical and digital realities makes augmented reality uniquely powerful.
The Role of AI in Augmented Reality

Artificial intelligence is the invisible engine that makes AR practical and scalable. Computer vision allows AR systems to recognize faces, objects, and environments. Machine learning enables personalization by adapting experiences based on user behavior. Meanwhile, real-time data processing ensures that digital elements respond instantly to changes in the physical world.
Because of AI, AR can now understand context. For example, an AR navigation app does not simply display arrows. Instead, it analyzes surroundings, traffic conditions, and user movement to provide accurate guidance. In the same way, retail AR applications can recommend products based on user preferences, body measurements, and past behavior.
Thus, augmented reality becomes intelligent rather than decorative.
AR in Everyday Life
AR has already entered daily life, often without users realizing it. Social media filters, camera effects, and interactive lenses are common examples. These tools rely on facial recognition, gesture tracking, and AI-driven animation to create engaging experiences.
At the same time, navigation apps use AR to guide users through unfamiliar spaces. Instead of reading maps, users follow visual cues overlaid on real streets. This reduces cognitive effort and improves accuracy. As adoption increases, augmented reality becomes less of a novelty and more of a utility.
AR in Education and Learning
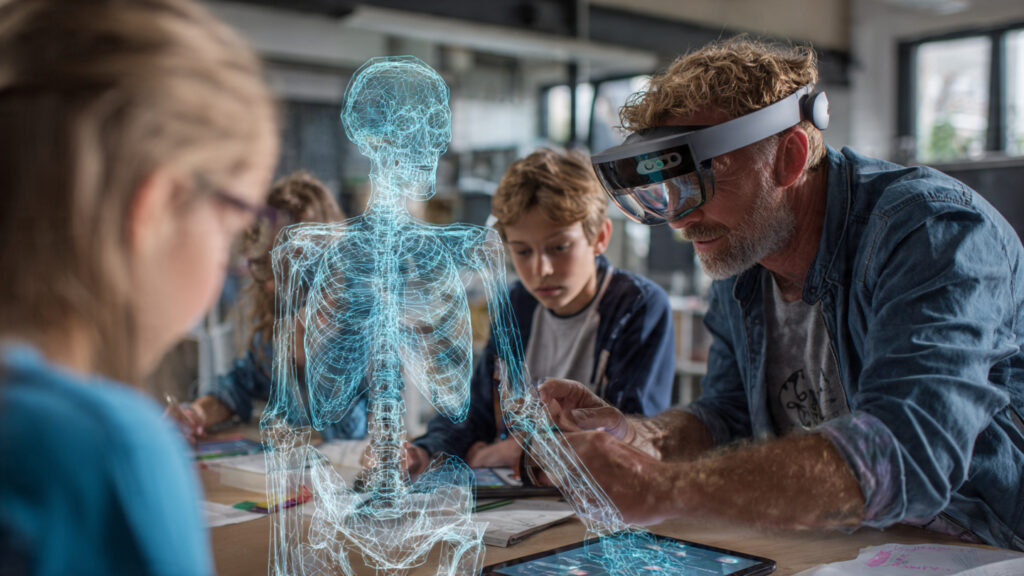

Education is one of the most transformative areas for AR Traditional learning often relies on static images and abstract explanations. AR changes this by turning lessons into interactive experiences. Students can visualize complex concepts, explore 3D models, and engage with content actively.
For example, biology students can explore the human body layer by layer. Engineering students can examine machine components in real scale. When combined with AI, AR adapts content based on learning speed and comprehension. This personalized approach improves understanding and retention.
Consequently, augmented reality supports inclusive education by catering to different learning styles.
AR in Healthcare
Healthcare applications of augmented reality are expanding rapidly. Surgeons use AR overlays during procedures to visualize internal structures without invasive exploration. Medical students practice using simulated patients with realistic anatomy. Meanwhile, rehabilitation programs use AR to guide exercises and track progress.
AI-powered augmented reality can analyze patient data and provide real-time feedback. This improves accuracy while reducing risk. In addition, remote consultations become more effective when doctors can visualize patient conditions through AR-assisted tools.
As healthcare systems adopt digital solutions, augmented reality enhances both precision and accessibility.
AR in Business and Industry
Businesses increasingly use augmented reality to improve efficiency and reduce costs. In manufacturing, AR guides workers through assembly processes with step-by-step visual instructions. This minimizes errors and shortens training time. In logistics, AR helps with inventory management by displaying real-time data directly in the workspace.
Customer support also benefits from AR. Instead of explaining solutions verbally, technicians can guide users visually. AI ensures that instructions adapt based on context and device type. As a result, service quality improves while operational expenses decrease.
Thus, augmented reality becomes a strategic business tool rather than a marketing gimmick.
AR in Retail and E-Commerce
Retail has embraced augmented reality to bridge the gap between online and offline shopping. Virtual try-ons allow customers to see clothing, accessories, or makeup before purchasing. Furniture retailers enable users to visualize products in their homes. These experiences reduce uncertainty and increase confidence.
AI enhances these applications by personalizing recommendations and improving accuracy. For example, body scanning ensures proper fit, while preference analysis suggests suitable styles. This combination of AR and AI reduces returns and improves customer satisfaction.
As consumer expectations evolve, augmented reality becomes essential for competitive retail experiences.
AR in Marketing and Branding
Marketing strategies increasingly rely on immersive experiences. Augmented reality allows brands to tell stories interactively rather than through static advertisements. Campaigns become memorable because users actively participate.
AI-driven analytics track engagement and optimize content dynamically. Instead of one-size-fits-all campaigns, brands deliver personalized AR experiences based on location, interests, and behavior. This leads to higher conversion rates and stronger emotional connections.
Therefore, augmented reality reshapes how brands communicate value in the digital age.
AR and Smart Cities
Smart cities rely on data-driven infrastructure to improve quality of life. AR plays a crucial role by visualizing information in real environments. Urban planners use AR to simulate development projects. Citizens access real-time data about transportation, energy usage, and public services.
AI-powered AR helps identify patterns and predict outcomes. For instance, traffic flow visualization improves urban mobility. Emergency response teams use AR to navigate complex environments quickly. As cities become smarter, augmented reality acts as the interface between data and decision-making.
AR in the Workplace
Remote and hybrid work environments benefit greatly from augmented reality. Virtual collaboration tools enable teams to interact with shared 3D models regardless of location. Training programs become immersive and hands-on without physical presence.
AI ensures that AR collaboration adapts to user roles and tasks. Productivity improves because information appears exactly when and where it is needed. This reduces interruptions and cognitive overload.
As work environments evolve, AR supports efficiency, creativity, and connection.
Challenges Facing Augmented Reality
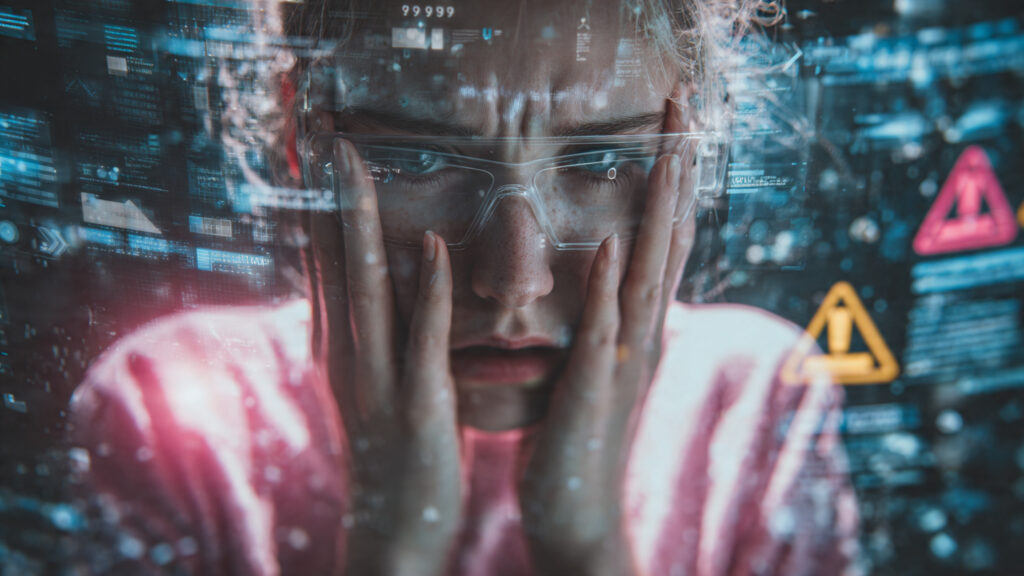

Despite its potential, AR faces several challenges. Hardware limitations restrict accessibility. Battery life, processing power, and device comfort remain concerns. Privacy issues arise due to constant data collection and environmental scanning.
Additionally, content creation requires specialized skills. Without standardization, experiences vary in quality. However, AI helps address these challenges by optimizing performance, automating content generation, and improving security.
Over time, these barriers are likely to decrease as technology matures.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations
AR raises important ethical questions. Continuous environmental scanning can collect sensitive data unintentionally. Facial recognition and location tracking must be handled responsibly.
AI-driven AR systems must prioritize transparency and user consent. Clear policies and strong regulations are essential. When designed ethically, AR enhances trust rather than eroding it.
Responsible development ensures long-term adoption and societal acceptance.
The Future of Augmented Reality
The future of AR lies in seamless integration. As devices become lighter and more powerful, AR will blend naturally into daily life. Smart glasses and wearable technology will replace handheld screens. AI will enable predictive experiences that anticipate user needs.
In the long term, AR may become the primary interface for digital interaction. Instead of screens, information will appear directly in physical space. This shift represents a fundamental change in how humans interact with technology.
AR and the AI-Driven World
In an AI-driven world, augmented reality acts as the visual layer of intelligence. AI processes data, while AR presents it intuitively. Together, they create systems that are both powerful and human-centered.
This synergy transforms productivity, learning, healthcare, and entertainment. Instead of overwhelming users with information, augmented reality simplifies complexity through contextual visualization.
Final Thoughts
Augmented reality is not just another digital trend. It represents a shift in how humans experience technology. When powered by artificial intelligence, augmented reality becomes adaptive, intelligent, and deeply integrated into everyday life.
As industries continue to evolve, augmented reality will play a central role in shaping the future of digital interaction. Those who understand and adopt it early will lead the next wave of innovation.