Prompt Engineering: The Skill That Decides How Powerful AI Really Is
Prompt engineering is not about writing clever sentences. It is about controlling how AI thinks, responds, and delivers results. The same AI model can give shallow, incorrect, or highly valuable output—depending entirely on the prompt it receives.
As AI tools become part of writing, coding, marketing, research, design, and automation, prompt engineering has turned into a core digital skill. People who understand it save hours of work, get more accurate results, and reduce AI errors significantly. Those who do not often assume the tool is weak, when the real issue is poor prompting.
This article focuses on practical prompt engineering, not theory. You will learn how prompts work, why results fail, real techniques that improve output, and which tools help you apply prompt engineering effectively.
What Prompt Engineering Really Means
Prompt engineering is the practice of structuring instructions in a way that guides an AI model toward the exact outcome you want.
A prompt is not just a question. It includes:
- Context
- Constraints
- Format expectations
- Role definition
- Output boundaries
Good prompt engineering reduces ambiguity. Poor prompts leave AI guessing—and guessing leads to hallucinations, generic responses, or irrelevant output.
Why Prompt Engineering Matters More Than the AI Model
Many users switch tools when results are bad. In reality, most AI failures come from unclear prompts, not weak models.
Prompt engineering helps:
- Reduce wrong or made-up answers
- Improve depth and accuracy
- Control tone, structure, and length
- Extract expert-level responses
- Make AI usable for real work
The difference between “okay AI” and “excellent AI” is almost always the prompt.
How AI Interprets Prompts
AI does not understand intent the way humans do. It predicts responses based on patterns.
If your prompt lacks:
- Clear goal
- Specific boundaries
- Proper framing
The AI fills gaps with assumptions. Prompt engineering removes those gaps.
Core Prompt Engineering Techniques That Actually Work
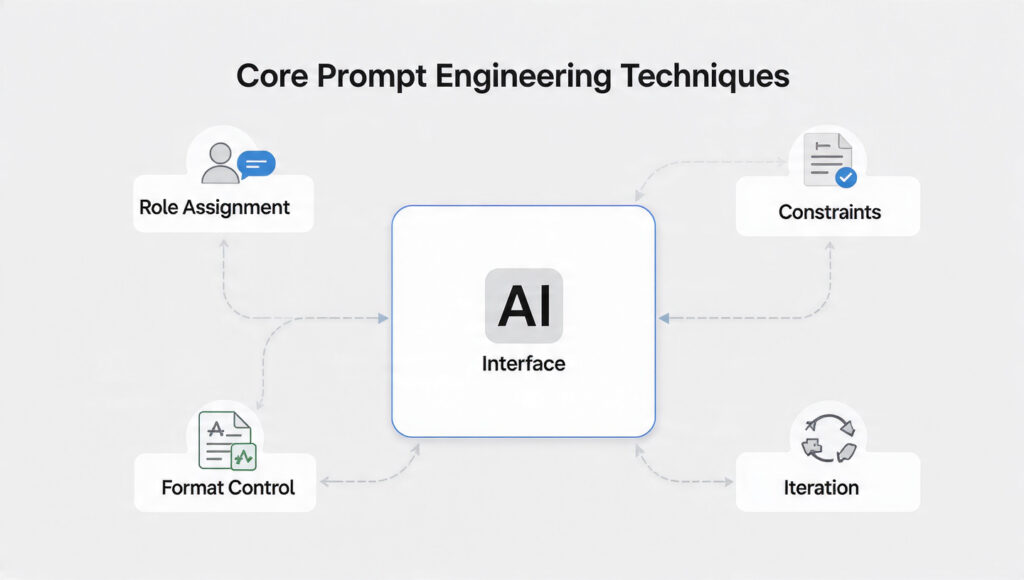
1. Role Assignment (Most Underrated Technique)
Telling AI who it is dramatically changes output quality.
Weak prompt:
Write an article about cybersecurity.
Engineered prompt:
Act as a cybersecurity analyst with enterprise experience. Write an article explaining real-world cybersecurity risks for small online businesses.
Why it works:
Roles activate domain-specific language, tone, and depth.
Tools where this works best:
ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Perplexity
2. Context Layering Instead of Long Questions
Many users write long prompts but still get weak results. The issue is missing structure, not length.
Effective prompts layer information:
- Background
- Objective
- Constraints
- Output format
Example:
You are helping a SaaS startup. The goal is to explain cloud outages to non-technical founders. Avoid jargon. Use real examples. Limit response to structured sections.
This approach outperforms long paragraphs of instructions.
3. Constraint-Based Prompting
AI performs better when it knows what not to do.
Useful constraints include:
- Word limits
- Tone restrictions
- Forbidden topics
- Output structure
Example:
Explain prompt engineering benefits. Avoid marketing language. No emojis. Use bullet points only.
This prevents generic, bloated responses.
4. Output Formatting Prompts
If you do not define format, AI chooses one for you—and often poorly.
You can demand:
- Tables
- Step-by-step lists
- Checklists
- Code blocks
- Headings only
Example:
Provide a comparison table with columns for tool name, use case, limitation.
This is essential for productivity workflows.
5. Iterative Prompt Refinement
Prompt engineering is not one-shot. Professionals refine prompts in cycles.
Effective method:
- Start broad
- Identify weakness
- Add one constraint
- Repeat
Instead of blaming AI, adjust the prompt.
Advanced Prompt Engineering Strategies
Chain-of-Thought Prompting (Controlled)
This encourages reasoning without forcing explanation.
Example:
Analyze the problem step by step internally, then provide the final answer only.
Useful for:
- Logic problems
- Planning
- Decision-making
Few-Shot Prompting
You show AI examples, not explanations.
Example:
Here are two examples of good prompts. Follow the same style for the next task.
This dramatically improves consistency.
Negative Prompting
Tell AI what bad output looks like.
Example:
Do not give generic advice. Avoid motivational language. No surface-level explanations.
This is highly effective for expert-level content.
Common Prompt Engineering Mistakes
- Asking vague questions
- Mixing multiple goals in one prompt
- Assuming AI understands intent
- Not defining audience
- Ignoring formatting needs
Fixing these alone improves results instantly.
Prompt Engineering for Real Use Cases

Content Creation
- Article outlines
- SEO-focused writing
- Research summaries
Helpful tools: ChatGPT, Jasper, Writesonic
Marketing & Growth
- Ad copy variations
- Email sequences
- Landing page messaging
Helpful tools: Copy.ai, Anyword, HubSpot AI
Coding & Technical Work
- Debugging prompts
- Code explanation
- API documentation
Helpful tools: ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, Codeium
Business & Strategy
- Market analysis
- Risk assessment
- Process automation
Helpful tools: Claude, Perplexity, Notion AI
Prompt Engineering Tools That Improve Workflow
- ChatGPT – Flexible, best for iterative prompting
- Claude – Strong at long-context reasoning
- Perplexity – Research-focused prompts with citations
- PromptPerfect – Optimizes prompts automatically
- FlowGPT – Community-tested prompt examples
These tools do not replace skill—but they amplify it.
Why Prompt Engineering Is Becoming a Career Skill
Companies now look for:
- Prompt designers
- AI workflow specialists
- Automation strategists
Prompt engineering sits between technical skill and creative thinking, making it valuable across roles.
Future of Prompt Engineering
As AI tools evolve, prompt engineering will shift from typing text to:
- Prompt templates
- Visual prompting
- Workflow-based prompting
However, the core skill—clear thinking translated into structured instructions—will remain essential.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering is not a trend. It is the control layer of AI. Those who master it do not just get better answers—they shape how AI works for them.
Instead of switching tools, upgrading plans, or blaming AI limitations, improving prompt engineering delivers immediate, measurable results. In a world where AI is everywhere, the ability to communicate with it effectively becomes a competitive advantage.